Blog
- Understanding the Natural Aging of Your Eyes
Presbyopia: Understanding the Natural Aging of Your Eyes
Presbyopia is a common eye condition where your eye gradually loses its ability to focus on nearby objects. This condition is a natural part of the aging process, with most people noticing symptoms in their early to mid-40s. The effects of presbyopia typically continue to worsen until around age 65.
A telltale sign of presbyopia is when you find yourself holding reading material, such as books or your phone, at arm's length to see the text clearly. If you experience these symptoms, a basic eye exam can confirm the diagnosis.
What Causes Presbyopia?
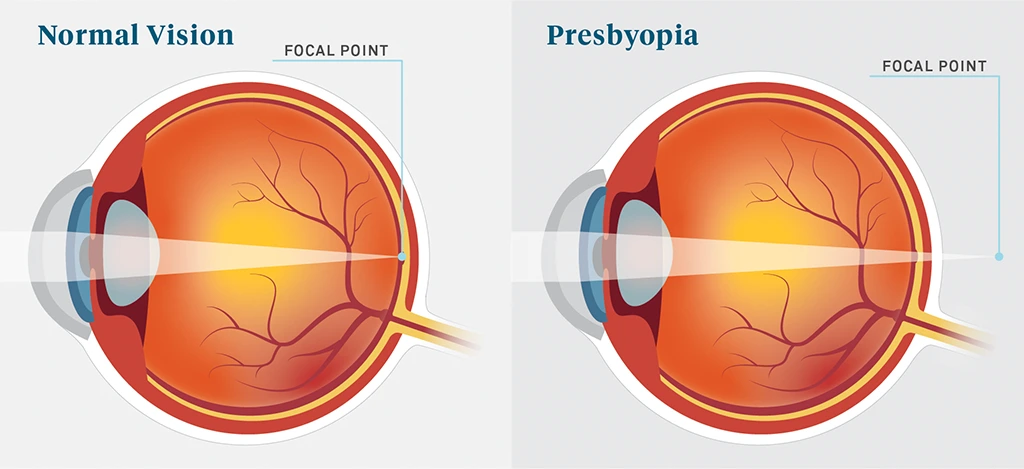
To understand the cause, it's helpful to know how your eye focuses. Light from an object enters your eye and is focused by the cornea and the lens onto the retina at the back of your eye.
Cornea: The clear, dome-shaped surface on the front of your eye.
Lens: A clear, flexible structure located behind the cornea.
Retina: The light-sensitive tissue lining the back of your eye.
For clear vision, the lens must change shape. When you look at a distant object, a circular muscle around the lens relaxes. When you look at something up close, this muscle constricts, causing the lens to curve and increase its focusing power.
Presbyopia occurs when the lens naturally hardens with age. This reduced flexibility makes it difficult for the lens to change shape, resulting in a decreased ability to focus on close-up images.
Common Symptoms of Presbyopia
The symptoms of presbyopia develop gradually. You might notice them first when you are tired or in dim lighting. Common signs include:
A tendency to hold reading materials farther away to see clearly.
Blurred vision at a normal reading distance.
Eyestrain, fatigue, or headaches after doing close-up work.
Diagnosis of Presbyopia
A comprehensive eye exam is used to diagnose presbyopia. This exam includes a refraction assessment to determine if you have nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, or presbyopia. Your eye doctor will have you look through a series of lenses to test your vision at both near and far distances.
In some cases, the doctor may use eye drops to dilate your pupils. This allows them to get a better view inside your eye and assess its overall health.
Treatment Options
The goal of presbyopia treatment is to compensate for your eyes' inability to focus on nearby objects. The most common solutions include eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery.
Eyeglasses
Progressive Lenses: These line-free multifocal lenses are a popular choice. They restore clear near vision and provide a smooth transition for vision at all distances.
Bifocal Lenses: Another option, though they offer a more limited range of vision than progressive lenses.
Reading Glasses: These are designed for close-up work only and are not meant to be worn all the time.
Anti-Reflective Coating: For any type of lens, this coating is highly recommended to reduce glare and eyestrain, especially when driving at night.
Contact Lenses
Multifocal Lenses: Available in soft or gas permeable materials, these lenses help you see clearly at different distances.
Monovision Lenses: This method uses a distance vision lens in one eye and a near vision lens in the other. Your brain learns to favor the appropriate eye for each task.
Surgery
For those who prefer not to wear glasses or contacts, surgical options are available. A common procedure is a Corneal Inlay, which is a small implant placed in the cornea of the non-dominant eye. This increases the depth of focus, improving near vision without significantly impacting distance vision.
Presbyopia: An Inevitable Part of Aging
Just as other bodily functions change with age, presbyopia is a natural and inevitable condition for most people. Fortunately, with various treatment options available, you can continue to enjoy activities like reading and using your phone without issue.
It is always important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and to get regular eye exams. The sooner an eye irregularity is identified, the better your chances are of addressing it and maintaining an independent lifestyle for years to come.



No Comments
Signup or login to leave a comment